What are you looking for?
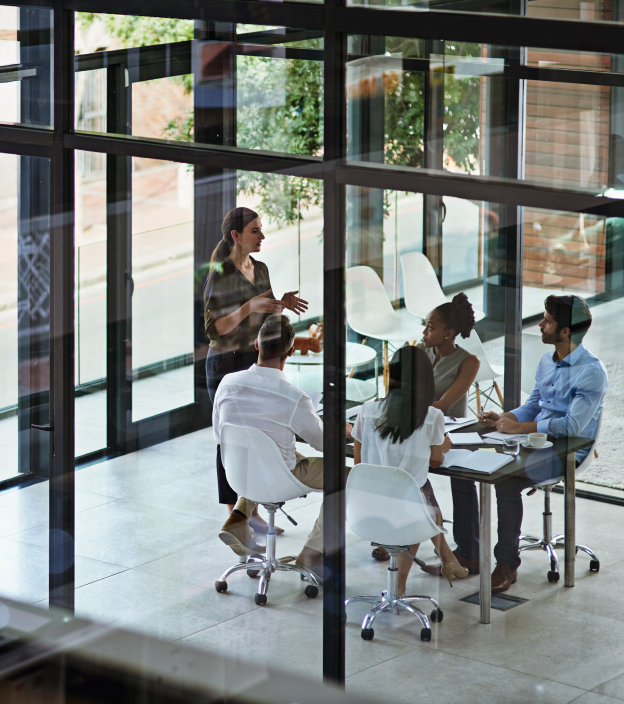
Upcoming Events
When
Where
Online via Zoom, 3:00 - 4:40 p.m., Manila time (GMT +8)
Organized by
Latest Highlights
Latest Publications

Sustainable Financing of Development and Infrastructure: A Handbook for Borrowers and Lenders is based on insights from the…
20 Mar 2024

Global health ODA of the Republic of Korea has consistently increased in line with the overall growth of ODA. During the COVID-19…
31 Dec 2023